5 Azimuth classification
Cell type classification using the azimuth method can be performed using
map_azimuth.R.
Let’s create an output directory to store the results.
mkdir step2_azimuthAnd check the input arguments
singularity exec -B $PWD cell_classification.sif \
Rscript /map_azimuth.R --helpUsage: map_azimuth.R [options]
Options:
--file=CHARACTER
RDS object file name
--batch=CHARACTER
Batch column. If provided, each group in from the batch columns is mapped to reference independently
--plan=CHARACTER
Strategy to resolve future [default= sequential]:
multisession
multicore
cluster
remote
transparent
--workers=NUMERIC
Number of workers used for parallelization
[default= 1]
--mem=NUMERIC
Maximum allowed total size (in GB) of global variables identified
[default= Inf]
--out=CHARACTER
Output file name [default= azimuth]
--path=CHARACTER
Output path to store results [default= .]
-h, --help
Show this help message and exitFurther data splitting and classification can be performed within map_azimuth.R
however, we’ll classify cells for each of the partitions we already created.
Although the
batchparameter is provided as an option to perform cell type classification withinmap_azimuth.R, we encourage users to previously split their data by batch usingsplit.Rand run sequential or parallel jobs for each batch as shown below to reduce RAM memory usage and reduce computation time
If
batchis used, thefuture.globals.maxSizeparameter from thefuturepackage can be manually changed via the--memargument when runningmap_azimuth.R. By default, this value is set to infinity to allow complete use of the allocated memory for each CPU. However, users may experience issues depending on the computing infrastructure. This value therefore can be changed in these cirmunstances. The--memvalue must be in Gb.
We can classify each batch within a loop using map_azimuth.R as follows:
for i in $(ls step1_split);
do
out=$(echo $i | awk 'gsub(".RDS", "")') # Use same base filename as output
singularity run -B $PWD cell_classification.sif \
Rscript /map_azimuth.R \
--file step1_split/${i} \
--path step2_azimuth \
--out ${out}
doneIn this example, the output is stored in step2_azimuth including each
Seurat object containing:
Cell type classification (
predicted.celltype.l2) + prediction scores (predicted.celltype.l2.scores) stored in the metadata-
Reference-based reductions:
- azimuth_spca: Supervised PCA
- azimuth_umap: UMAP generated using the WNN graph
A new assay called
predicted_ADTcontaining imputed protein data based on RNA
Additionally, plots for the azimuth_spca and azimuth_umap reductions are included
as outputs for exploratory data analysis.
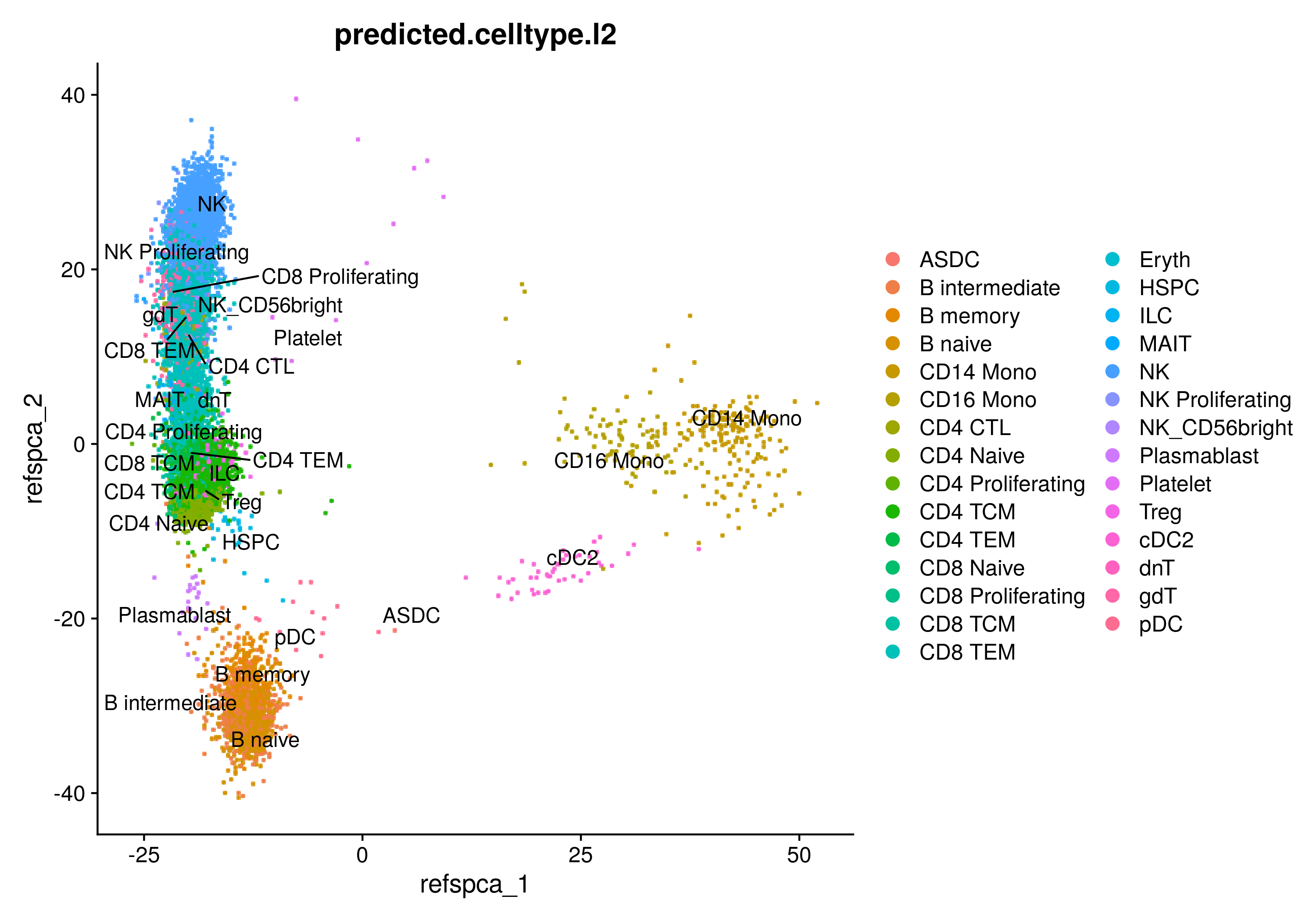
PCA embeddings projected onto the reference supervised PCA
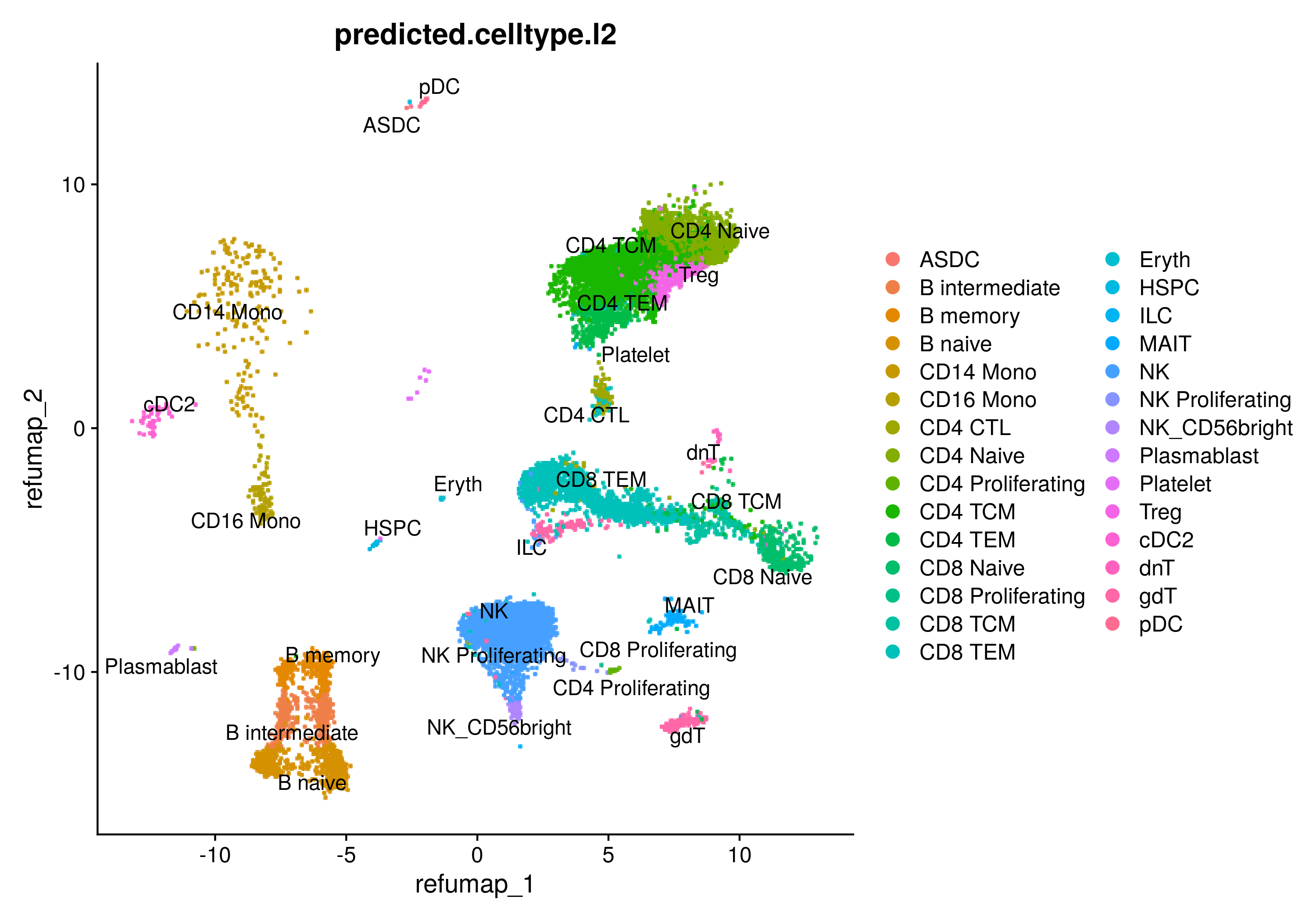
Query dataset projected onto the reference UMAP
5.2 SGE example
The following array job code in SGE (Sun Grid Engine) can be used as a guide to classify each pool in individual jobs. This code snippet was used to classify multiple Seurat objects (75 pools) from the OneK1K dataset.
#$ -N clasify_cells
#$ -q short.q
#$ -l mem_requested=50G
#$ -S /bin/bash
#$ -r yes
#$ -cwd
#$ -o results/2021-10-28_cell_type_annotation
#$ -e results/2021-10-28_cell_type_annotation
# mkdir results/2021-10-28_cell_type_annotation
cd $SGE_O_WORKDIR
# Set environmental variables
input=results/2021-10-28_pools
output=results/2021-10-28_cell_type_annotation
# Get job info
echo "JOB: $JOB_ID TASK: $SGE_TASK_ID HOSTNAME: $HOSTNAME"
# Get basefile name
files=($(ls ${input} | grep ".RDS"))
i="$(($SGE_TASK_ID-1))"
filename=${files[$i]}
filename=$(echo $filename | sed 's/.RDS//')
echo "Classifying: $filename"
# Run main command
singularity exec -B $SGE_O_WORKDIR bin/cell_classification.sif \
Rscript /map_azimuth.R \
--file ${input}/${filename}.RDS \
--out ${filename}_out \
--path ${output}If we save the previous code into a file (e.g. run_azimuth.sh), we can launch
an array job iterating for each pool name
qsub -t 1-75 bin/run_azimuth.sh
# -t Vector of length equal to the number of pools (.RDS files)5.3 SLURM example
Likewise, we can run the same code using a SLURM scheduler as follows:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -J azimuth
#SBATCH -N 1
#SBATCH -n 1
#SBATCH --time=0:30:00
#SBATCH --mem=40GB
#SBATCH --error=job.%J.err
#SBATCH --output=job.%J.out
#SBATCH --mail-type=END,FAIL
#SBATCH --mail-user=l.c.m.michielsen@lumc.nl
# Clear the environment from any previously loaded modules
module purge
module add container/singularity/3.7.3/gcc.8.3.1
# Set environmental variables
input=DataGroningen/step1_split
output=DataGroningen/output_Azimuth
# Get job info
echo "Starting at `date`"
echo "JOB: $SLURM_JOB_ID TASK: $SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID"
# Get basefile name
files=($(ls ${input} | grep ".RDS"))
i="$SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID"
filename=${files[$i]}
filename=$(echo $filename | sed 's/.RDS//')
echo "Classifying: $filename"
# Run main command
singularity exec -B $PWD cell_classification.sif \
Rscript /map_azimuth.R \
--file ${input}/${filename}.RDS \
--batch lane \
--out ${filename}_out \
--path ${output}If we save the previous code into a file (e.g. run_azimuth.sbatch), we can launch
an array job iterating for each batch
sbatch -a 0-30 run_azimuth.sbatch
# -a Vector of length equal to the number .RDS files